Lời giải
Bài tập: Cho hàm số \( y = \frac{x - 1}{x + 2} \) có đồ thị \((C)\). Gọi \( I \) là giao điểm của 2 tiệm cận của \((C)\). Xét tam giác đều \( \Delta ABI \) có hai đỉnh \( A, B \) thuộc \((C)\), đoạn thẳng \( AB \) có độ dài bằng:
\(\text{A. } \sqrt{6} \quad \text{B. } 2\sqrt{3} \)
\(\text{C. } 2 \quad \text{D. } 2\sqrt{2} \)
(Đề thi 2018, Mã đề 101, câu 45)
\(\text{A. } \sqrt{6} \quad \text{B. } 2\sqrt{3} \)
\(\text{C. } 2 \quad \text{D. } 2\sqrt{2} \)
(Đề thi 2018, Mã đề 101, câu 45)
Lời giải:
- \( y = \frac{x - 1}{x + 2} \) \(= \frac{x + 2 - 3}{x + 2} = 1 - \frac{3}{x + 2} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow y - 1 = - \frac{3}{x + 2} \).
\( \Leftrightarrow \begin{cases} Y= -\frac{3}{X} \\ Y = y - 1 \\ X = x + 2 \end{cases} \)
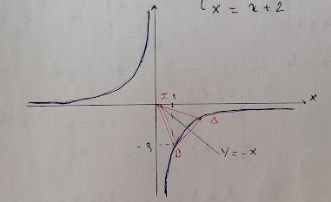
- \( A, B \in (C)\) thỏa yêu cầu \( \Rightarrow \widehat{xIA} = -15^{\circ} \) \(\Rightarrow \tan(\widehat{xIA}) = \sqrt{3} - 2 \) \( \Rightarrow \) Phương trình đường thẳng \(IA: y = (\sqrt{3} - 2)x \)
- Tọa độ điểm \( A \): \(\begin{cases}y = (\sqrt{3} - 2) x \\y = -\frac{3}{x}\end{cases}\) \(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}(\sqrt{3} - 2)x = -\frac{3}{x} \\y = -\frac{3}{x}\end{cases}\)
\(\Rightarrow \begin{cases}x^2 = 3(2 - \sqrt{3}) \\y = -\frac{3}{x}\end{cases} \) \( \Rightarrow A \left(\sqrt{3(2 - \sqrt{3})}, -\frac{3}{2 - \sqrt{3}}\right)\)
- \(AB = IA = \sqrt{3(2 - \sqrt{3}) + \frac{3}{2 - \sqrt{3}}} = \sqrt{\frac{3\left[(2 - \sqrt{3})^2 + 1\right]}{2 - \sqrt{3}}} \)
\(= \sqrt{\frac{3(7 - 4\sqrt{3} + 1)}{2 - \sqrt{3}}} = \sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy chọn \(\boxed{B}\).